Importance of Color Management In Printing
Colours are an integral part of both life and printing. They bring vibrancy, dimension, and meaning to the world around us. Colours symbolize the essence and characteristics of objects, making them recognizable and appealing. Imagine life without colours—it would be dull and uninspiring. Similarly, in printing, colours enhance the overall appeal and purpose of the final output.This blog explores the importance of colours management in printing, focusing on its aesthetic and technical aspects, and why it is a critical element in producing high-quality printed materials.
Why Is Colours Management Important?
Colours management is a vital process that ensures the accurate reproduction of colours in printed materials. It enhances the final output by reducing ink consumption, improving quality, and increasing productivity. A well-executed Colours management system minimizes errors, reduces the need for reprints, and ensures consistent results.
For businesses, Colours management also plays a key role in maintaining brand identity. Accurate Colours reproduction ensures that brand colours remain consistent across all printed materials, reinforcing brand guidelines and delivering the desired results every time.
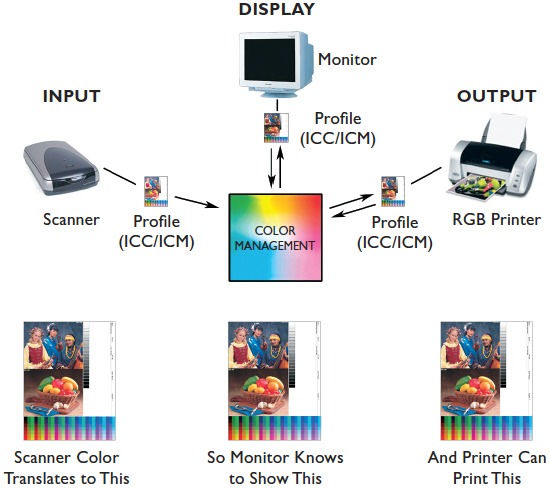
The Role of Colours Management in Pre-Press
Colours management in the pre-press stage allows for precise Colours simulation across the production workflow. This involves calibrating devices like scanners, monitors, and printers, as well as creating and applying ICC (International Colours Consortium) profiles. These profiles enable printers to produce accurate colours that match the artwork, ensuring the printed result aligns with the designer’s vision.
Understanding the Colours Management Process
Colours management involves mapping the Colours characteristics of every device in the imaging chain to achieve consistent Colours reproduction. The goal is to match Colours appearance as closely as possible from input (e.g., camera or scanner) to output (e.g., printer) and across devices.
Objectives of Colours Management:
- Achieving consistent Colours reproduction across devices.
- Ensuring colours appear the same on screens, printed materials, and other media.
- The Four Components of a Colours Management System
- An ICC-based Colours management system consists of four key components:
Profile Connection Space (PCS):
A device-independent Colours space, usually CIELAB, where Colours conversions take place.
Device Profiles:
These are files that describe the unique Colours properties of devices like monitors, scanners, and printers. Each device’s profile ensures accurate Colours representation in the imaging workflow.
Colours Management Module (CMM):
The CMM is the engine that converts Colours data between different profiles or Colours spaces.
Rendering Intent:
This determines how colours are mapped when converting between Colours spaces. Different intents (e.g., Perceptual or Relative Colours metric) can be chosen based on the image and desired results.
RGB vs. CMYK in Printing
Understanding the difference between RGB and CMYK is essential in the printing process.
RGB (Red, Green, Blue): Used for digital displays, RGB is an additive Colours model where colours are created by adding light.
CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Key/Black): Used for printing, CMYK is a subtractive Colours model where colours are created by combining inks.
Key Differences:
- RGB is ideal for digital media, while CMYK is best for print materials.
- RGB colours need to be converted to CMYK for accurate printing.
- RGB values range from 0 to 255, whereas CMYK values range from 0 to 100%.
- For printed formats, CMYK is always recommended to ensure accurate Colours representation.
Steps for Efficient Colours Management at Print Image
At Print Image, we take critical care in ensuring efficient Colours management throughout the printing process. Here are the six steps we follow:
- Profiled Conversions: Assign ICC profiles during image conversion or scanning to minimize colour conversions.
- Monitor Calibration: Calibrate monitors for optimal brightness, white point, and gamma settings.
- Colour Settings in Software: Use proper colour settings in design software to preserve embedded profiles.
- Soft Proofing: Simulate print appearance on screen for adjustments.
- Printer Driver Settings: Use software like Photoshop or Lightroom to ensure compatibility with output profiles.
- Controlled Environment: Evaluate proofs in neutral lighting to minimize external light influence.










