
RGB vs CMYK: A Complete Guide to Colour Profiles
What is RGB?
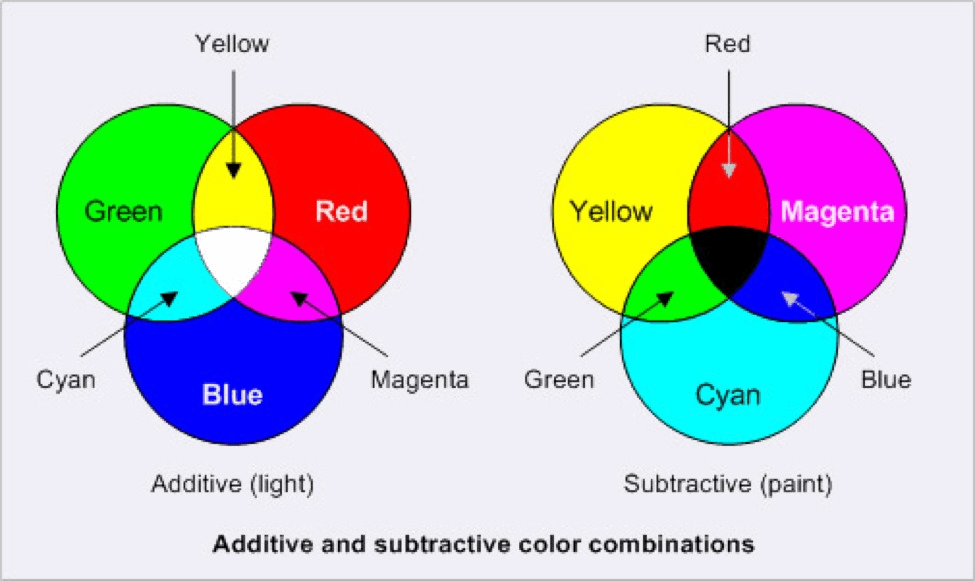
RGB stands for Red, Green, and Blue, the Colour mode used for digital screens. It’s an additive Colour model where varying intensities of red, green, and blue light create a wide spectrum of Colours.
- White: All Colours at maximum intensity (RGB 255, 255, 255).
- Black: All Colours at minimum intensity (RGB 0, 0, 0).
Common Uses of RGB:
- Digital screens (computers, TVs, mobile devices)
- Web design and apps
- Online branding and ads
- Social media graphics
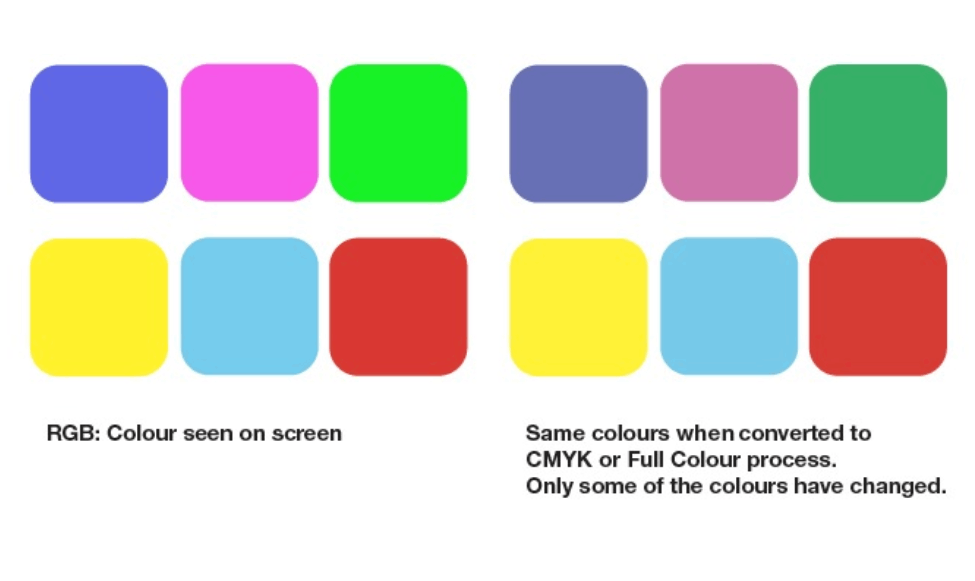
Common Mistakes in Using RGB and CMYK:
- Using RGB for Print: Designing in RGB for print projects often leads to Colour mismatches during production. Always set your Colour mode to CMYK for print materials.
- Skipping Colour Conversion: Converting files from RGB to CMYK without Colour adjustment can result in dull or altered Colours. Adjust hues and saturation for accurate results.
- Ignoring Proofs: Neglecting to check proofs can lead to unsatisfactory prints. Always review the final design on a calibrated screen or proof printer.
Types of Paper
1.Coated Paper: Has a smooth finish with a layer of clay or gloss, ideal for vibrant colors and sharp images, commonly used for brochures, menus, and leaflets.
2.Uncoated Paper: Lacks gloss, offering a natural texture, suitable for stationery, photocopying, and laser printing.
Subtypes of Uncoated Paper:
- Laid Paper: Textured, used for premium stationery.
- Wove Paper: Smooth, high-quality for business use.
- Bond Paper: Affordable, used for office tasks.
- Recycled Paper: Eco-friendly, made from reusable pulp.
Paper GSM: GSM measures the weight and thickness of paper. Common ranges in India include:
- Coated Paper: 90-170 GSM (lightweight), 210-350 GSM (heavyweight).
- Uncoated Paper: 47-120 GSM.
- Packaging Boards: 170-400 GSM.
Paper Sizes: Common sizes include:
- Coated and Uncoated Paper: 23”x36”, 25”x36”, 30”x40”.
- Boards: 23”x36”, 31.5”x41.5”.
For quick reference, here are some standard A-series sizes:
| Size | Dimensions (mm) | Dimensions (in) |
| A1 | 594 X 841 | 23.4 X 33.1 |
| A2 | 420 X 594 | 16.5 X 23.4 |
| A3 | 297 X 420 | 11.7 X 16.5 |
| A4 | 210 X 297 | 8.3 X 11.7 |

What is CMYK?
CMYK stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (Black). It’s the Colour mode used for printing, based on the subtractive Colour model where inks combine to create a range of Colours.
- White: No ink (CMYK 0%, 0%, 0%, 0%).
- Black: Maximum ink levels.
Common Uses of CMYK:
- Printed materials (business cards, posters, brochures)
- Merchandise and packaging
- Advertising (flyers, banners)
- Custom apparel (t-shirts, uniforms)
Key Differences Between RGB and CMYK:
| Features | RGB | CMYK |
| Primary Colours | Red, Green, Blue | Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black |
| Colour Mixing | Additive | Subtractive |
| Applications | Digital screens | Print materials |
| Colour Vibrancy | More vibrant and wide-ranging | Less vibrant |
| File Formats | JPEG, PNG, GIF | PDF, EPS |
Understanding Colour Spaces:
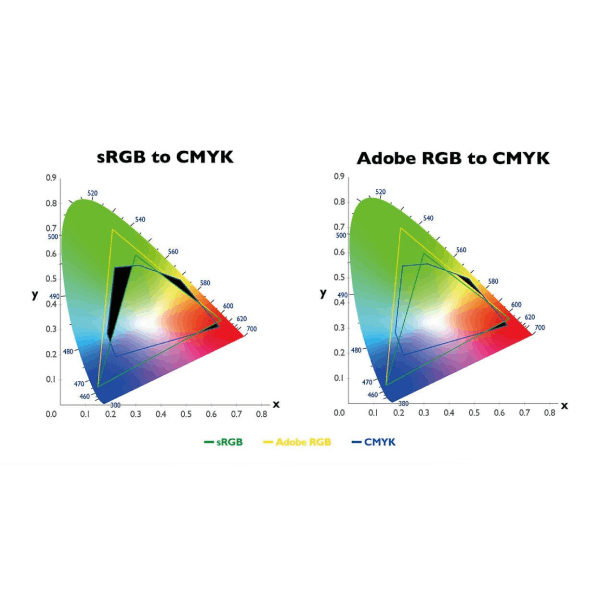
A Colour space is a specific range of Colours that can be produced using a Colour model. Both RGB and CMYK have unique Colour spaces, with the most common being sRGB and Adobe RGB for digital work.
- sRGB: Ideal for online content and compatible with most screens.
- Adobe RGB: Offers a broader Colour spectrum but requires a compatible monitor and is better suited for professional print materials.
Why Choose CMYK for Printing?
The RGB Colour gamut is broader than CMYK, meaning some RGB Colours, especially bright or fluorescent tones, cannot be accurately reproduced in CMYK. This is why designing in CMYK from the start is crucial for print projects.
How to Avoid Issues
- Create files in CMYK mode using professional design software.
- Adjust Colour balance and levels during conversion for accurate results.
- Use commercial printing proofs to verify the final output.
Setting Up CMYK in Design Software
Here’s how to configure CMYK settings in popular design tools:
- Adobe Photoshop: Choose CMYK Colour mode when creating a new document or convert an existing one via Image > Mode > CMYK Colour.
- Adobe Illustrator: Set the document Colour mode to CMYK during creation and export as PDF/X-1a:2001 for print.
- Adobe InDesign: Export files with the PDF/X-1a:2001 preset for CMYK compatibility.
- Microsoft Publisher: Navigate to File > Info > Commercial Print Settings to select the CMYK Colour model.
Tips for Flawless Printing
- DO use printed CMYK swatches to check Colours.
- DO proof designs on a calibrated monitor.
- DO print a commercial proof to ensure accuracy.
- DON’T rely on desktop printers to preview Colours—they often emulate RGB settings.





